Yes! You can use AI to fill out Form 2106, Employee Business Expenses
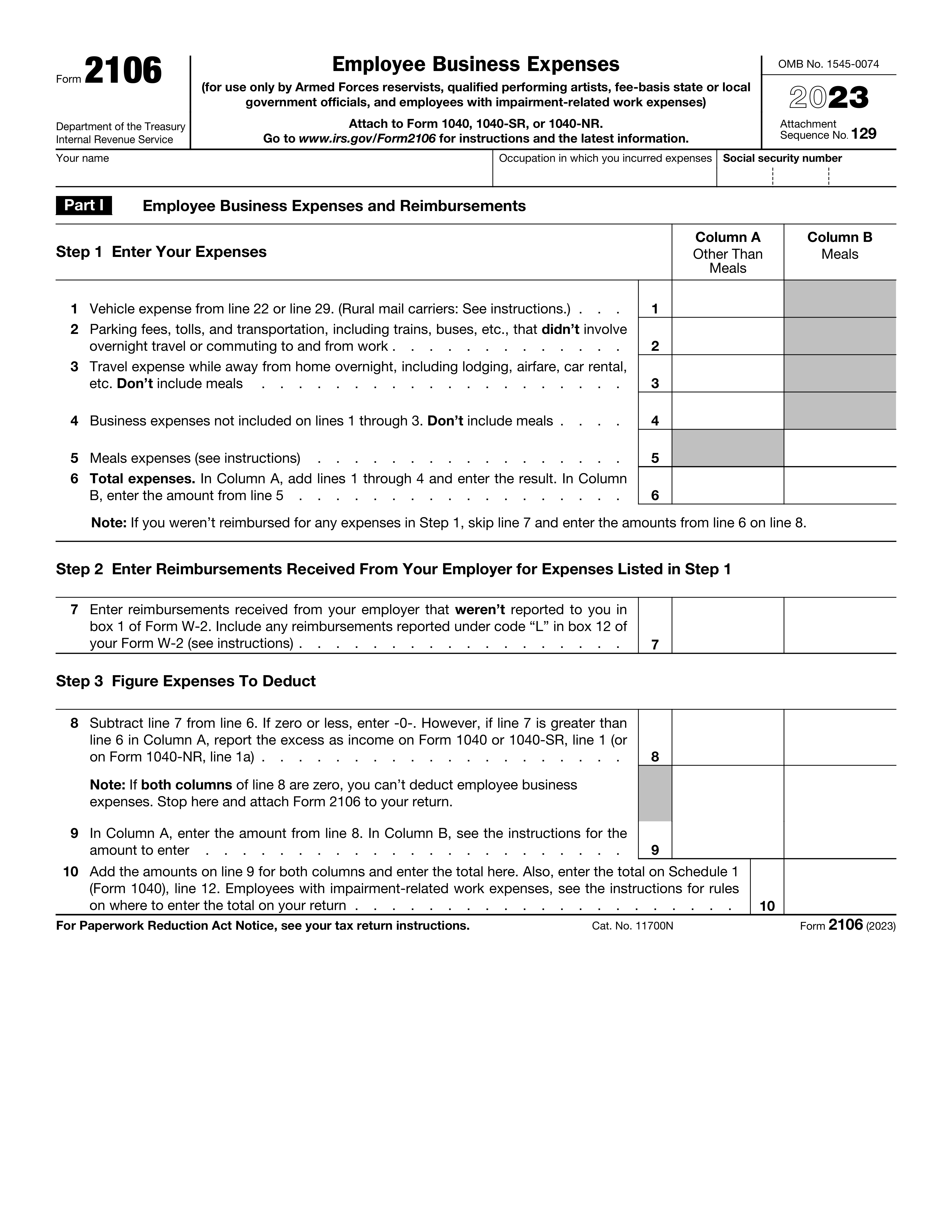
Form 2106, Employee Business Expenses, is used by qualified individuals to report their business-related expenses. This form is essential for calculating deductions that can reduce taxable income, ensuring that eligible expenses are accounted for.
Our AI automatically handles information lookup, data retrieval, formatting, and form filling.
It takes less than a minute to fill out Form 2106 using our AI form filling.
Securely upload your data. Information is encrypted in transit and deleted immediately after the form is filled out.
Form specifications
| Form name: | Form 2106, Employee Business Expenses |
| Form issued by: | Department of the Treasury, Internal Revenue Service |
| Number of fields: | 87 |
| Number of pages: | 2 |
| Version: | 2023 |
| Instructions: | https://www.irs.gov/pub/irs-pdf/i2106.pdf |
| Filled form examples: | Form Form 2106 Examples |
| Language: | English |
| Categories: | business forms, employee forms, employee expense forms, business expense forms |
Instafill Demo: filling out a legal form in seconds
How to Fill Out Form 2106 Online for Free in 2026
Are you looking to fill out a FORM 2106 form online quickly and accurately? Instafill.ai offers the #1 AI-powered PDF filling software of 2026, allowing you to complete your FORM 2106 form in just 37 seconds or less.
Follow these steps to fill out your FORM 2106 form online using Instafill.ai:
- 1 Visit instafill.ai site and select Form 2106.
- 2 Enter your name and occupation.
- 3 Fill in your business expenses and reimbursements.
- 4 Complete vehicle expenses if applicable.
- 5 Sign and date the form electronically.
- 6 Check for accuracy and submit the form.
Our AI-powered system ensures each field is filled out correctly, reducing errors and saving you time.
Why Choose Instafill.ai for Your Fillable Form 2106 Form?
Speed
Complete your Form 2106 in as little as 37 seconds.
Up-to-Date
Always use the latest 2026 Form 2106 form version.
Cost-effective
No need to hire expensive lawyers.
Accuracy
Our AI performs 10 compliance checks to ensure your form is error-free.
Security
Your personal information is protected with bank-level encryption.
Frequently Asked Questions About Form Form 2106
Form 2106 allows the deduction of various business expenses for certain employees. These expenses include: vehicle expenses, parking fees, tolls, transportation, travel expenses while away from home overnight, business expenses not included on lines 1 through 3, and meals expenses (with certain limitations).
Form 2106 is specifically designed for use by Armed Forces reservists, qualified performing artists, fee-basis state or local government officials, and employees with impairment-related work expenses.
Column A is for entering the total of all expenses listed in Part I. Column B is for entering the amount of expenses that are not meals. It is important to accurately report both total expenses and non-meal expenses to calculate the allowable deductions.
To calculate the expenses to deduct in Part III, subtract the reimbursements received from your employer (line 7) from the total expenses (line 6). If the result is zero or less, enter -0-. If the result is greater than line 6 in Column A, report the excess as income on Form 1040 or 1040-SR.
Part II of Form 2106 requires detailed information about the vehicle(s) used for business purposes. This includes the date the vehicle was placed in service, the total miles driven during the year, business miles, the percentage of business use, and commuting miles. Accurately reporting this information is crucial for determining the allowable vehicle expense deductions.
Yes, if you choose to use the standard mileage rate, you must complete Section B of Part II. If you prefer to calculate your expenses based on actual expenses, you must complete Section C.
You should keep records of all expenses, including receipts, invoices, and other documentation that proves the business purpose and amount of each expense.
Form 2106 should be attached to your Form 1040, 1040-SR, or 1040-NR and filed by the same deadline as your income tax return.
Yes, but there are specific rules and limitations for claiming a deduction for meals expenses. Refer to the instructions for Part I, Step 5 of Form 2106 for details.
The OMB No. for Form 2106 is 1545-0074.
Compliance Form 2106
Validation Checks by Instafill.ai
1
Form 2106 Usage Criteria
Ensures that Form 2106 is exclusively utilized by individuals who are eligible, such as Armed Forces reservists, qualified performing artists, fee-basis state or local government officials, or employees with impairment-related work expenses. It verifies the occupation and status of the taxpayer to confirm eligibility. The check prevents ineligible taxpayers from using the form, thereby maintaining compliance with IRS regulations. It also provides guidance to users about who is qualified to file Form 2106.
2
Suspension of Miscellaneous Itemized Deductions
Confirms that miscellaneous itemized deductions subject to the 2% floor under section 67(a) are currently suspended and are not being claimed on the form. This validation ensures adherence to the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act provisions, which suspend such deductions. It prevents the taxpayer from making erroneous claims that could result in miscalculations or potential penalties. The check also helps maintain the integrity of the tax return by ensuring only allowable deductions are claimed.
3
Rural Mail Carriers' Reimbursements
Verifies that rural mail carriers are correctly treating qualified reimbursements as allowable expenses on Line 1 of Form 2106. This check ensures that these specific taxpayers are in compliance with the rules pertaining to their occupation. It also helps rural mail carriers to accurately report their expenses, thus avoiding potential issues with the IRS. The validation confirms that the reported amounts reflect the actual qualified reimbursements received.
4
Exclusion of Commuting Expenses
Checks that commuting expenses, which are generally non-deductible, are not included as deductible expenses on Line 2 of the form. This validation is crucial as it ensures that taxpayers do not mistakenly claim nondeductible commuting costs as work-related expenses. It helps maintain the accuracy of the expense report and prevents the filing of incorrect tax information. The check also educates taxpayers about the types of expenses that are not permissible as deductions.
5
Lodging and Transportation Expenses for Overnight Travel
Validates that lodging and transportation expenses for overnight travel away from the taxpayer's tax home are entered correctly on Line 3. This check ensures that the taxpayer is complying with IRS rules regarding travel expenses. It helps in the accurate calculation of deductible travel expenses, which can be a complex area of tax law. The validation also assists taxpayers in distinguishing between personal and business travel expenses.
6
Other Job-Related Expenses
Ensures that any job-related expenses that do not fit into the categories provided on the form are accurately captured on Line 4. This includes a thorough review of the expenses to confirm they are indeed related to the employment and have not been accounted for in other sections of the form. The AI cross-references these expenses with common examples of 'other' expenses to ensure validity. It also checks for proper documentation and receipts that support the entries made on this line.
7
Allowable Meals Expense
Confirms that the amount entered on Line 5 for meals is either the standard meal allowance or the actual expenses incurred, whichever is applicable. The AI applies the 50% limitation rule to ensure that only the eligible portion of the meal expenses is claimed. It also verifies the dates and locations of travel to ensure that the standard meal allowance corresponds with the current federal per diem rates. Additionally, it checks for any discrepancies between claimed expenses and provided receipts.
8
Reimbursements Not Reported
Verifies that any reimbursements received for business expenses that are not reported in box 1 of Form W-2 are correctly entered on Line 7. The AI cross-checks with other documentation such as expense reports and employer statements to confirm the accuracy of these entries. It also ensures that these reimbursements are indeed not included in the taxable income reported on Form W-2 and are related to the business expenses claimed.
9
Business Meal Deductions
Checks that only 50% of the business meal expenses are being deducted on Line 9, in accordance with the general rules for business meal deductions. The AI reviews the meal expenses to ensure they are legitimate business expenses and calculates the correct 50% limit to be applied. It also validates that the total amount claimed on Line 9 does not exceed the calculated eligible amount after the 50% reduction.
10
Special Rules Application
Validates that the special rules for Armed Forces reservists, fee-basis state or local government officials, qualified performing artists, and disabled employees are applied correctly when calculating deductible business expenses. The AI checks for proper identification and qualification under these special categories and applies the specific rules and exceptions that pertain to each. It also ensures that any additional documentation required for these special circumstances is provided and accurate.
11
Ensures that vehicle information in Section A is complete and accurate.
The AI software meticulously reviews Section A to ensure that all vehicle information provided is complete and accurate. It cross-references vehicle details with official databases when possible to confirm the accuracy of the make, model, and year. The software also checks for consistency in the vehicle identification number (VIN) and license plate information. It alerts the user if any fields are incomplete or if the data does not align with standard vehicle information formats.
12
Confirms that the standard mileage rate or actual expenses method is correctly applied in Sections B and C.
The AI software confirms that the user has selected either the standard mileage rate or the actual expenses method for calculating vehicle expenses in Sections B and C. It ensures that the chosen method is consistently applied throughout the form and that the calculations are based on the correct rates for the tax year in question. The software also checks for common errors, such as mixing methods or applying outdated rates, and provides guidance for correction if needed.
13
Verifies that depreciation details provided in Section D are in accordance with the depreciation limits for the current year.
The AI software verifies that the depreciation details entered in Section D are in line with the current year's depreciation limits. It checks the accuracy of the depreciation calculation, ensuring that it adheres to the Modified Accelerated Cost Recovery System (MACRS) or any other applicable depreciation method. The software also reviews the start date of depreciation to confirm that it aligns with the date the vehicle was placed in service and flags any discrepancies for user review.
14
Checks that the Section 179 Deduction and Special Depreciation Allowance are correctly calculated and applied.
The AI software checks that the Section 179 Deduction and Special Depreciation Allowance, if claimed, are correctly calculated and applied in accordance with the current tax laws. It ensures that the amounts entered do not exceed the statutory limits and that the vehicle qualifies for such deductions. The software also verifies that the total deduction is properly reflected in the overall expense calculation and alerts the user to any inconsistencies.
15
Validates that all required records and documentation to support the expenses claimed are maintained and available.
The AI software validates that the user has maintained and has available all required records and documentation to support the expenses claimed on the form. It prompts the user to confirm the existence of logs, receipts, and other necessary documents. The software also provides a checklist of required documentation for the user's reference and ensures that the claimed expenses are substantiated by this documentation to avoid issues during potential audits.
Common Mistakes in Completing Form 2106
Employees may overlook the fact that they are not eligible to file Form 2106 for business expenses. Eligibility is limited to Armed Forces reservists, qualified performing artists, fee-basis state or local government officials, and employees with impairment-related work expenses. Failure to identify eligibility may result in incorrect reporting and potential penalties. To avoid this mistake, carefully review the instructions and eligibility requirements before filling out the form.
Commuting expenses, such as transportation costs between home and work, are often overlooked when filing Form 2106. These expenses are deductible if they are necessary and ordinary for the employee's job. Neglecting to enter commuting expenses may result in underreporting and potential lost deductions. To ensure proper reporting, employees should keep detailed records of their commuting expenses and include them in the appropriate section of the form.
Another common mistake is reporting lodging and transportation expenses for personal trips instead of business trips. These expenses are only deductible if they are incurred while traveling for business. To avoid this mistake, employees should carefully review the instructions and ensure that they are only reporting expenses that are directly related to their job. Keeping detailed records and receipts can help support the deduction of these expenses.
Form 2106 only lists certain types of expenses in the provided sections. However, employees may have other job-related expenses that are not listed. Failure to report these expenses may result in underreporting and lost deductions. To avoid this mistake, employees should carefully review the instructions and consider all expenses that are necessary and ordinary for their job. If expenses are not listed on the form, they should be reported in the "Other Expenses" section.
Employees may receive reimbursements from their employer for expenses listed in Step 1. Failure to report these reimbursements may result in double-dipping and potential penalties. To avoid this mistake, employees should report the reimbursements they have received in the appropriate section of the form. This will ensure that they are not claiming a deduction for expenses that have already been reimbursed.
Business meal expenses are subject to a 50% limitation for tax deduction. However, some taxpayers may incorrectly apply this limitation to the entire meal expense, rather than just the portion considered as food or beverages. To avoid this mistake, ensure that only the cost of food and beverages is subjected to the 50% limitation, while the cost of taxes, tips, and other service charges are fully deductible. Keep detailed records of these expenses to support your deductions.
Another common mistake is miscalculating the total amount of expenses eligible for deduction. This can occur when taxpayers fail to include all relevant expenses or incorrectly calculate the costs. To prevent this error, carefully review the instructions for the form and ensure that all qualifying expenses are included in the calculation. Keep detailed records of all expenses, including receipts, invoices, and other supporting documentation.
The standard mileage rate is provided for taxpayers' convenience when calculating vehicle expenses. However, some taxpayers may mistakenly use the standard rate for personal use instead of business use. To avoid this mistake, ensure that you are using the correct rate for business use and maintain detailed records of your business miles, including the date, destination, and purpose of each trip. Keeping accurate records will help you to accurately calculate your vehicle expenses and maximize your tax deductions.
Proper record keeping is essential for accurately reporting business expenses on the Employee Business Expenses form. Some taxpayers may neglect to maintain adequate records, making it difficult to support their deductions. To prevent this mistake, keep detailed records of all business expenses, including receipts, invoices, and other supporting documentation. Maintaining accurate records will help you to accurately report your expenses and avoid potential audits or disputes with the IRS.
The Employee Business Expenses form requires taxpayers to provide complete and accurate information in Sections A, B, C, and D of Part II - Vehicle Expenses. Some taxpayers may overlook this requirement or provide incomplete or inaccurate information, leading to potential errors or discrepancies. To avoid this mistake, ensure that you provide all required information, including the make, model, and year of the vehicle, the date of purchase, and the business use percentage. Keeping accurate records and double-checking your entries will help you to avoid potential errors and ensure that your tax deductions are properly reported.
Employees may overlook the limits and thresholds for depreciation and Section 179 deductions when reporting business expenses. Depreciation is the allocation of the cost of a business asset over its useful life, while Section 179 allows for the deduction of the full cost of certain qualifying assets in the year they are purchased. Failing to adhere to these limits and thresholds can result in underreporting or overreporting of expenses. To avoid this mistake, employees should familiarize themselves with the current depreciation limits and Section 179 deduction thresholds and ensure they accurately apply these limits to their reported expenses.
The special depreciation allowance (SDA) is a tax incentive that allows businesses to deduct a larger percentage of the cost of certain assets in the first year. Employees may not fully understand the rules surrounding SDA and how it applies to their business expenses. Failing to properly apply SDA can result in missed deductions or incorrect reporting. To avoid this mistake, employees should familiarize themselves with the rules surrounding SDA and consult with a tax professional to ensure they are accurately applying this tax incentive to their reported expenses.
Saved over 80 hours a year
“I was never sure if my IRS forms like W-9 were filled correctly. Now, I can complete the forms accurately without any external help.”
Kevin Martin Green
Your data stays secure with advanced protection from Instafill and our subprocessors



Robust compliance program
Transparent business model
You’re not the product. You always know where your data is and what it is processed for.
ISO 27001, HIPAA, and GDPR
Our subprocesses adhere to multiple compliance standards, including but not limited to ISO 27001, HIPAA, and GDPR.
Security & privacy by design
We consider security and privacy from the initial design phase of any new service or functionality. It’s not an afterthought, it’s built-in, including support for two-factor authentication (2FA) to further protect your account.
Fill out Form 2106 with Instafill.ai
Worried about filling PDFs wrong? Instafill securely fills 2106 forms, ensuring each field is accurate.