Yes! You can use AI to fill out Form 1099-SA, Distributions from HSA/MSA
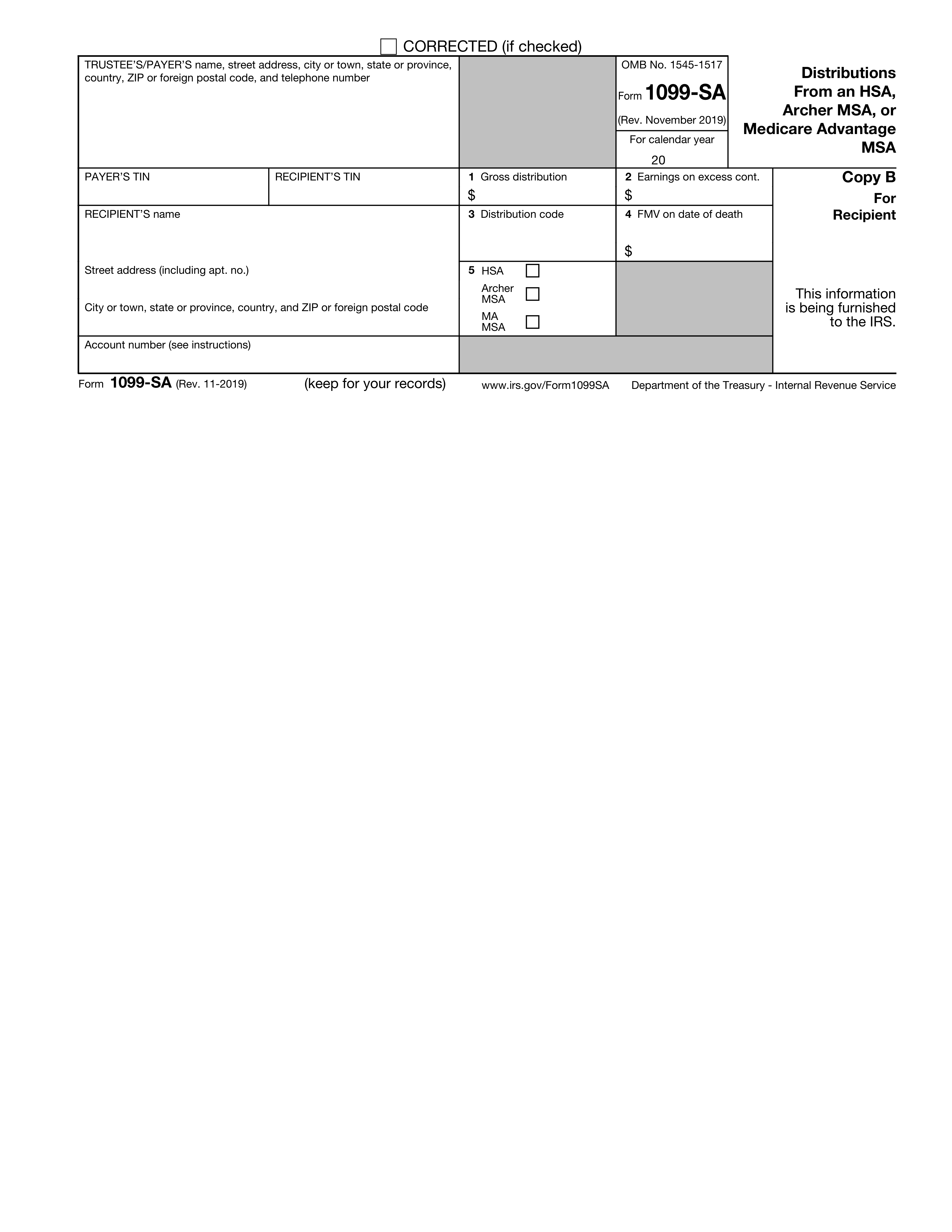
Form 1099-SA is a tax document that reports distributions from Health Savings Accounts (HSAs), Archer Medical Savings Accounts (MSAs), or Medicare Advantage (MA) MSAs. It is important for taxpayers to report these distributions on their tax returns, as they may be taxable or reportable events.
Our AI automatically handles information lookup, data retrieval, formatting, and form filling.
It takes less than a minute to fill out 1099-SA using our AI form filling.
Securely upload your data. Information is encrypted in transit and deleted immediately after the form is filled out.
Form specifications
| Form name: | Form 1099-SA, Distributions from HSA/MSA |
| Form issued by: | Department of the Treasury - Internal Revenue Service |
| Number of fields: | 50 |
| Number of pages: | 5 |
| Version: | 2019 |
| Filled form examples: | Form 1099-SA Examples |
| Language: | English |
| Categories: | 1099 forms |
Instafill Demo: How to fill out PDF forms in seconds with AI
How to Fill Out 1099-SA Online for Free in 2026
Are you looking to fill out a 1099-SA form online quickly and accurately? Instafill.ai offers the #1 AI-powered PDF filling software of 2026, allowing you to complete your 1099-SA form in just 37 seconds or less.
Follow these steps to fill out your 1099-SA form online using Instafill.ai:
- 1 Visit instafill.ai and select 1099-SA
- 2 Enter payer's and recipient's TIN
- 3 Input recipient's name and address
- 4 Fill in account number if applicable
- 5 Report gross distribution amount
- 6 Indicate earnings on excess contributions
- 7 Select appropriate distribution code
- 8 Enter FMV on date of death if needed
- 9 Check HSA, Archer MSA, or MA MSA box
- 10 Sign and date the form electronically
- 11 Check for accuracy and submit form
Our AI-powered system ensures each field is filled out correctly, reducing errors and saving you time.
Why Choose Instafill.ai for Your Fillable 1099-SA Form?
Speed
Complete your 1099-SA in as little as 37 seconds.
Up-to-Date
Always use the latest 2026 1099-SA form version.
Cost-effective
No need to hire expensive lawyers.
Accuracy
Our AI performs 10 compliance checks to ensure your form is error-free.
Security
Your personal information is protected with bank-level encryption.
Frequently Asked Questions About Form 1099-SA
Form 1099-SA is an IRS tax form used to report distributions made from a Health Savings Account (HSA), Archer Medical Savings Account (MSA), or Medicare Advantage MSA to the IRS and the account holder. This form is used to ensure that distributions from these accounts are reported for tax purposes and to verify that they are used for qualified medical expenses.
Form 1099-SA should be received by individuals who have taken distributions from their HSA, Archer MSA, or Medicare Advantage MSA during the tax year. The financial institution that manages the account is responsible for issuing the form to both the account holder and the IRS.
When you receive Form 1099-SA, you should review it for accuracy and retain it for your records. You will use the information reported on the form to complete your tax return, specifically Form 8889 for HSAs or Form 8853 for Archer MSAs and Medicare Advantage MSAs. The form will help you determine if the distributions you received are taxable and if you need to pay any additional taxes or penalties.
There are multiple copies of Form 1099-SA, each intended for a different purpose. Copy A is sent to the IRS by the financial institution. Copy B is provided to the account holder for their records and to use when filing their taxes. Copy C may be kept by the financial institution for their records, and there may be additional copies that vary by institution, such as a state copy if required for state tax purposes.
Box 1 on Form 1099-SA represents the total amount of distributions made from the HSA, Archer MSA, or Medicare Advantage MSA during the tax year. This amount includes all distributions made for qualified medical expenses as well as any other distributions. It is important to note that only distributions not used for qualified medical expenses may be taxable.
Box 2 on Form 1099-SA indicates the amount of earnings on excess contributions. This box shows the earnings on excess contributions that are included in the gross distribution reported in box 1. These earnings are taxable and must be reported on the individual's tax return.
Box 3 of Form 1099-SA contains distribution codes that represent the type of distribution the individual has received from their HSA, Archer MSA, or Medicare Advantage MSA. These codes help determine how the distribution should be reported on the individual's tax return. Common codes include: 1 for normal distributions, 2 for excess contributions, 3 for disability, 4 for death distribution other than code 6, 5 for prohibited transaction, and 6 for death distribution after year of death to a non-spouse beneficiary.
Box 4 of Form 1099-SA reports the fair market value (FMV) of the account as of the date of death if the account holder passed away during the year. This information is used for tax reporting purposes, particularly in determining the taxable portion of the distribution and the inclusion in the decedent's final income tax return.
Form 1099-SA is used to report distributions from health savings accounts (HSAs), Archer Medical Savings Accounts (Archer MSAs), and Medicare Advantage MSAs (MA MSAs). These accounts are tax-advantaged accounts designed to help individuals save for and pay medical expenses.
To report a distribution from an HSA, Archer MSA, or MA MSA on your tax return, you must use Form 8889 for HSAs or Form 8853 for Archer MSAs and MA MSAs. You will need to include the information from Form 1099-SA, such as the total distribution amount, earnings on excess contributions, and the distribution code, to determine the taxable portion of the distribution and any potential penalties. The forms and instructions will guide you through the reporting process and help you calculate any taxes or deductions related to your account distributions.
If you use your Health Savings Account (HSA) or Archer Medical Savings Account (MSA) distribution for non-qualified expenses, the amount you use will be subject to both income tax and an additional 20% tax penalty. Non-qualified expenses are those that do not meet the IRS criteria for medical expenses. It's important to keep records of your medical expenses to show that distributions were used for qualified medical expenses to avoid these taxes.
Yes, you can roll over funds from an HSA or Archer MSA to another HSA or Archer MSA. However, you must complete the rollover within 60 days after the date you received the distribution. Only one rollover is allowed per 12-month period. Direct trustee-to-trustee transfers between HSAs or Archer MSAs are not considered rollovers, and there is no limit to the number of these transfers you can make.
The tax implications of inheriting an HSA, Archer MSA, or Medicare Advantage MSA (MA MSA) depend on your relationship to the deceased. If you are the spouse of the deceased, you can treat the HSA as your own. If you are not the spouse, the account ceases to be an HSA, and the fair market value of the account becomes taxable to you in the year the account owner died. The additional 20% tax penalty does not apply in this case, but the amount is included in your income.
Earnings on excess contributions to your HSA or Archer MSA are taxable. You must report these earnings on your tax return for the year in which the earnings occurred. The excess contributions and the earnings on them are subject to an excise tax of 6% per year as long as they remain in the account. You should file Form 5329, 'Additional Taxes on Qualified Plans (Including IRAs) and Other Tax-Favored Accounts,' to report and calculate the excise tax.
The deadline to correct excess contributions to an HSA or Archer MSA is your tax filing deadline, including extensions, for the year in which the excess contribution was made. To correct the excess contribution, you must withdraw the excess amount and any earnings on it before the deadline. The excess contribution is taxed as income in the year it was contributed, but the additional 6% excise tax can be avoided if the correction is made by the deadline.
The excise tax for excess contributions to a Health Savings Account (HSA) or an Archer Medical Savings Account (MSA) is 6%. This tax applies to contributions that exceed the annual contribution limits. Taxpayers must pay this excise tax when they file their federal income tax return using Form 5329, 'Additional Taxes on Qualified Plans (Including IRAs) and Other Tax-Favored Accounts.' It is important for individuals to monitor their contributions to avoid this tax and to withdraw excess contributions before the tax filing deadline if an over-contribution occurs.
If you receive a Form 1099-SA with incorrect information, you should contact the payer, which is typically the trustee or custodian of your HSA or MSA, as soon as possible to request a corrected form. The payer is responsible for issuing a corrected Form 1099-SA, which will have the 'Corrected' box checked at the top of the form. It is important to ensure that the information on the form matches your own records, as discrepancies can affect your tax liability.
More information about Form 1099-SA and its instructions can be found on the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) website. The IRS provides detailed instructions for the form, which include information on how to report distributions from an HSA or MSA, how to handle specific box entries on the form, and guidance on reporting requirements. Taxpayers can download the instructions directly from the IRS website or contact the IRS directly for additional assistance.
The purpose of including the payer's and recipient's Taxpayer Identification Numbers (TINs) on Form 1099-SA is for identification and tax reporting purposes. The payer's TIN identifies the trustee or custodian of the HSA or MSA that is reporting the distribution, while the recipient's TIN identifies the individual who received the distribution. These numbers are used by the IRS to match the reported information with the individuals' tax returns and to ensure accurate tax reporting and compliance.
If you have questions about reporting on Form 1099-SA, you should first refer to the instructions provided by the IRS for the form. If your questions are not resolved by the instructions, you can contact the IRS directly for assistance. Additionally, if your questions pertain to the specifics of the distribution or the information provided by the payer, you should contact the trustee or custodian of your HSA or MSA who issued the Form 1099-SA. For complex tax situations, it may also be advisable to consult with a tax professional or accountant.
Compliance 1099-SA
Validation Checks by Instafill.ai
1
Ensures that the 'Calendar Year' field is filled with the correct year for which the distributions are being reported.
This validation check ensures that the 'Calendar Year' field on Form 1099-SA is accurately completed with the appropriate year that corresponds to the distributions being reported. It verifies that the year entered is not in the future or a past year unrelated to the reported distributions. The check is crucial for maintaining the temporal accuracy of the form and ensuring that the IRS receives the correct information for the specified tax year.
2
Verifies that the 'VOID' checkbox is marked only if the form is void and should not be processed.
This validation check verifies that the 'VOID' checkbox on Form 1099-SA is marked only when the form is intended to be voided and should not be processed by the IRS. It ensures that the checkbox is not mistakenly marked, which could lead to the form being disregarded. The check is essential to prevent accidental voiding of the form and to maintain the integrity of the filing process.
3
Confirms that the 'CORRECTED' checkbox is marked if the form is correcting a previously filed Form 1099-SA.
This validation check confirms that the 'CORRECTED' checkbox is marked on Form 1099-SA when the form is submitted to correct information on a previously filed Form 1099-SA. It ensures that the IRS is aware that the form is an amendment to prior information, facilitating accurate record-keeping and adjustments. The check is vital for the proper processing of corrections and for avoiding confusion with original filings.
4
Checks that the 'Trustee/Payer's Information' section contains the complete name and address, including city, state, province, country, and ZIP or foreign postal code.
This validation check ensures that the 'Trustee/Payer's Information' section of Form 1099-SA includes all necessary details such as the complete name and address of the trustee or payer. It verifies that the city, state, province, country, and ZIP or foreign postal code are provided and accurate. This check is crucial for the IRS to have the correct contact information for the entity responsible for the distribution, which is necessary for any potential follow-up or clarification.
5
Validates that the 'Trustee/Payer's Information' section includes a correct telephone number.
This validation check validates that a correct telephone number is included in the 'Trustee/Payer's Information' section of Form 1099-SA. It ensures that the number provided is in the correct format and is a valid point of contact. This check is important for enabling the IRS or other interested parties to reach out to the trustee or payer if there are any questions or issues with the reported distributions.
6
Ensures that the 'Payer's TIN' in the 'Trustee/Payer's Information' section is a valid Taxpayer Identification Number.
This validation check ensures that the 'Payer's TIN' field in the 'Trustee/Payer's Information' section of Form 1099-SA is filled with a valid Taxpayer Identification Number. It verifies the format and digit composition of the TIN to confirm its legitimacy. The check also cross-references the number with official databases when possible to ensure its authenticity. Any discrepancies or invalid entries are flagged for correction.
7
Confirms that the 'Recipient's Information' section contains a valid TIN for the recipient.
This validation check confirms that the 'Recipient's Information' section of Form 1099-SA includes a valid Taxpayer Identification Number for the recipient. It scrutinizes the TIN to ensure it adheres to the appropriate format and contains the correct number of digits. The check also aims to validate the TIN against relevant records to ensure it corresponds to the named recipient. Invalid or missing TINs are highlighted for further action.
8
Verifies that the 'Recipient's Information' section includes the recipient's full name, street address, apartment number if applicable, city or town, state or province, country, and ZIP or foreign postal code.
This validation check verifies that the 'Recipient's Information' section of Form 1099-SA is fully completed with the recipient's full name and complete address details. It checks for the presence of the street address, apartment number if applicable, city or town, state or province, country, and ZIP or foreign postal code. The check ensures that all fields are populated and formatted correctly, and that the information provided matches the recipient's known details.
9
Checks that the 'Account Number' is present if it is not reported on Copy A for the IRS.
This validation check ensures that the 'Account Number' field is populated on Form 1099-SA if the information is not already reported on Copy A for the IRS. It checks for the presence of an account number and confirms that it is consistent with the payer's records. If the account number is missing or inconsistent, the check flags this for review and correction to ensure accurate reporting.
10
Validates that Box 1 contains the gross distribution amount in dollars and is a numeric value.
This validation check validates that Box 1 of Form 1099-SA accurately reflects the gross distribution amount in dollars and confirms that the entry is a numeric value. It ensures that the amount is properly formatted with no non-numeric characters and that it represents a plausible figure for a distribution from an HSA or MSA. Any errors or inconsistencies in the gross distribution amount are identified for rectification.
11
Ensures that Box 2 contains the earnings on excess contributions in dollars and is a numeric value.
This validation check ensures that the information entered in Box 2 of Form 1099-SA accurately represents the earnings on excess contributions and is expressed in a numeric dollar amount. It verifies that no non-numeric characters are present and that the value is formatted correctly as a monetary amount. This check is crucial to maintain the integrity of the financial information reported to the IRS and to prevent errors in tax calculations related to Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) or Medical Savings Accounts (MSAs).
12
Confirms that Box 3 contains the appropriate distribution code.
The validation process for Box 3 on Form 1099-SA involves confirming that the distribution code entered is one of the valid codes as specified by the IRS. It checks that the code corresponds to the type of distribution made from the HSA or MSA. This ensures accurate reporting and compliance with IRS regulations, as well as facilitating correct tax treatment of the distribution.
13
Verifies that Box 4 contains the fair market value on the date of death in dollars and is a numeric value.
For Box 4 of Form 1099-SA, this validation check verifies that the entry represents the fair market value of the account on the date of the account holder's death, and that it is provided as a numeric dollar value. It ensures that the amount is entered without any non-numeric characters and reflects the accurate market value, which is essential for proper tax reporting and for beneficiaries to understand the value of the inherited HSA or MSA.
14
Checks that Box 5 has the correct box checked to indicate the type of account: HSA, Archer MSA, or MA MSA.
This check is designed to ensure that the correct account type is indicated in Box 5 of Form 1099-SA. It involves verifying that one, and only one, of the boxes corresponding to HSA, Archer MSA, or MA MSA is marked, reflecting the nature of the account from which distributions were taken. This is important for the IRS to determine the applicable tax rules and for the taxpayer to receive the correct tax treatment.
15
Validates that all required fields are completed before the form is filed with Form 1096 to the IRS.
This comprehensive validation confirms that all mandatory fields on Form 1099-SA are filled out prior to submission along with Form 1096. It checks for completeness and accuracy of the taxpayer's information, ensuring that no essential details are missing, which could lead to processing delays or penalties. This step is critical for maintaining compliance with IRS filing requirements and for the timely processing of the form.
Common Mistakes in Completing 1099-SA
Filers sometimes forget to include Copy A of Form 1099-SA when submitting it along with Form 1096 to the IRS. It is crucial to remember that Copy A is the official IRS copy and must be included when filing. To avoid this mistake, filers should organize their documents carefully and double-check that all required copies are attached before mailing. Using a checklist can also help ensure that no document is overlooked during the filing process.
Entering the wrong calendar year for distributions on Form 1099-SA can lead to confusion and potential tax issues for the account holder. It is important to verify the distribution dates and ensure that they correspond to the correct tax year before completing the form. Filers should cross-reference their records with the distribution statements provided by the trustee or payer to confirm the accuracy of the tax year reported.
If a mistake is made on Form 1099-SA and a corrected form needs to be issued, it is essential to check the 'VOID' or 'CORRECTED' box at the top of the form. This indicates to the IRS that the form is either voided or a corrected version of a previously filed form. To prevent this oversight, filers should review the form thoroughly before submission and mark the appropriate box if the form is being voided or corrected. Keeping a record of all forms issued, including those that are voided or corrected, can also help maintain accurate filing.
The trustee or payer's full name and address are required fields on Form 1099-SA and must be completed accurately. Omitting this information can result in processing delays or misdirected correspondence. Filers should ensure that they have the correct and complete details of the trustee or payer before filling out the form. It is advisable to use pre-printed forms or labels if available, to minimize the risk of errors in entering this information.
The trustee or payer's telephone number is an important piece of information that should be included on Form 1099-SA. Neglecting to provide this number can hinder communication between the IRS and the trustee or payer if any issues arise. Filers should make sure to obtain the correct telephone number and include it on the form. It is a good practice to verify the number for accuracy and clarity before submitting the form to the IRS.
The payer's Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN) is a critical piece of information required on Form 1099-SA. Failure to include the TIN can lead to processing delays and potential penalties. To avoid this mistake, double-check the payer's TIN before submission and ensure it is accurately entered in the appropriate field. It is also advisable to verify the TIN against official documents or previous tax forms to confirm its correctness.
Omitting the recipient's Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN) on Form 1099-SA can result in incorrect tax reporting and issues for the recipient. To prevent this error, always request the recipient's TIN in advance and confirm its accuracy. Enter the TIN carefully in the designated area on the form. If the recipient's TIN is not available, follow the IRS guidelines for submitting forms without a TIN.
Providing incomplete recipient's name or address details can lead to misdirected or undeliverable tax documents. Ensure that the recipient's full legal name is used as it appears on their tax identification documents. Additionally, verify the address for completeness, including apartment or suite numbers if applicable. Review the information with the recipient if necessary to confirm its accuracy before filing the form.
Neglecting to include the recipient's city, state, and ZIP code is a common oversight that can hinder the delivery of tax-related correspondence. Always complete the address section in its entirety, including city, state, and ZIP code. Use the United States Postal Service's ZIP code lookup tool if you are unsure of the correct ZIP code. This ensures that all mailed documents reach the recipient without delay.
The account number is an essential identifier on Form 1099-SA, especially when the payer has multiple accounts for the recipient. Failing to enter the account number on Copy A can cause confusion and misallocation of distributions. To avoid this, always include the account number as it appears on the account statement or other related documents. Double-check the number for accuracy to ensure proper reporting and record-keeping.
Entering an incorrect gross distribution amount in box 1 can lead to discrepancies in tax calculations and reporting. To avoid this mistake, double-check the distribution statements provided by the financial institution managing the HSA or MSA. Ensure that the amount entered matches the total distributions received during the tax year. It is also advisable to cross-reference this amount with personal records and bank statements to confirm its accuracy before submitting the form.
Miscalculating earnings on excess contributions in box 2 can result in incorrect tax liability. To prevent this error, carefully review the IRS guidelines on how to calculate earnings on excess contributions. Use accurate interest rates and contribution data, and consider using tax software or consulting with a tax professional to ensure the calculation is correct. Keep detailed records of all contributions to the account to simplify this process.
Using the wrong distribution code in box 3 can lead to confusion about the nature of the distribution and potentially trigger an IRS inquiry. Familiarize yourself with the IRS distribution codes and their meanings as outlined in the instructions for Form 1099-SA. Verify the type of distribution taken and choose the code that accurately reflects the transaction. If uncertain about which code to use, seek clarification from the financial institution or a tax advisor.
Misreporting the fair market value on the date of death in box 4 can have significant tax implications for the estate or beneficiaries. To avoid this error, obtain an accurate valuation of the account as of the date of death, which may require the assistance of the financial institution holding the account. Ensure that this value is reported correctly on the form. If the account has multiple beneficiaries, it may also be necessary to allocate the fair market value proportionally.
Failing to check the correct account type box in box 5 can result in improper tax treatment of the distributions. Before completing the form, confirm whether the distribution is from a Health Savings Account (HSA) or a Medical Savings Account (MSA). Check the appropriate box that corresponds to the type of account from which the distribution was made. Reviewing account documentation or consulting with the financial institution can help ensure the correct box is checked.
Recipients often overlook the importance of reviewing the instructions for tax reporting provided with Form 1099-SA. This can lead to errors in reporting distributions from Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) or Medical Savings Accounts (MSAs) on their tax returns. To avoid this mistake, recipients should carefully read the instructions that accompany Form 1099-SA to understand how to report these distributions correctly. It is also advisable to consult with a tax professional if there is any confusion regarding the tax implications of these distributions.
Trustees or payers sometimes fail to refer to the general instructions for Form 1099-SA, which can result in incorrect or incomplete forms being issued. It is crucial for trustees and payers to familiarize themselves with the IRS's general instructions for this form to ensure accurate reporting of distributions. Regularly reviewing the latest instructions and updates from the IRS can help prevent errors. Additionally, using IRS-approved software for form preparation can assist in reducing mistakes.
Both recipients and trustees/payers may neglect to visit the IRS website for additional resources and guidance related to Form 1099-SA. The IRS website offers a wealth of information, including frequently asked questions, publications, and the latest updates on tax laws that can help in accurately completing and understanding the form. To avoid this oversight, it is recommended to regularly check the IRS website for any new information regarding HSA and MSA distributions and to utilize the available tools and resources for assistance in tax reporting.
Saved over 80 hours a year
“I was never sure if my IRS forms like W-9 were filled correctly. Now, I can complete the forms accurately without any external help.”
Kevin Martin Green
Your data stays secure with advanced protection from Instafill and our subprocessors



Robust compliance program
Transparent business model
You’re not the product. You always know where your data is and what it is processed for.
ISO 27001, HIPAA, and GDPR
Our subprocesses adhere to multiple compliance standards, including but not limited to ISO 27001, HIPAA, and GDPR.
Security & privacy by design
We consider security and privacy from the initial design phase of any new service or functionality. It’s not an afterthought, it’s built-in, including support for two-factor authentication (2FA) to further protect your account.
Fill out 1099-SA with Instafill.ai
Worried about filling PDFs wrong? Instafill securely fills 1099-sa forms, ensuring each field is accurate.