Style Replication
Show the AI how you write, and it replicates your voice in every form. Upload previously filled documents or paste writing samples for key fields - and Instafill.ai matches your tone, vocabulary, and formatting automatically.
Overview
When Instafill.ai form filler generates text for description fields, narrative sections, or summaries, the output is accurate but sometimes can look unnatural. Overly formal phrasing, repetitive sentence structures, vocabulary that clearly came from a machine. For professionals who need documents to read as authentic and human-written, this means editing every output before it's ready.
Style Replication (Examples) fixes this. There are two ways to teach the AI your voice:
- Upload previously filled forms. When you upload a PDF form, you can also upload completed versions of the same form. The AI extracts field values from those documents and uses them as reference examples automatically.
- Add examples manually. In the Field Editor, paste or type writing samples for specific fields. Useful when you don't have previously filled forms or want fine-grained control over individual fields.
Either way, the AI analyzes your tone, vocabulary, sentence structure, and formatting - then replicates your voice when generating text. The result sounds like you wrote it.
Fields without examples still fill accurately using the standard AI. Fields with examples fill with your specific voice, making the output indistinguishable from text you wrote yourself.
How It Works
Method 1: Upload previously filled forms
When you upload a blank form to Instafill.ai, you can also upload completed versions of the same form - forms you or your team filled out previously. The AI reads how those forms were filled: your phrasing, your terminology, the length and structure of your answers. Then, when it fills the blank form with new data, it writes in that same voice. Your facts change, but the tone stays yours.
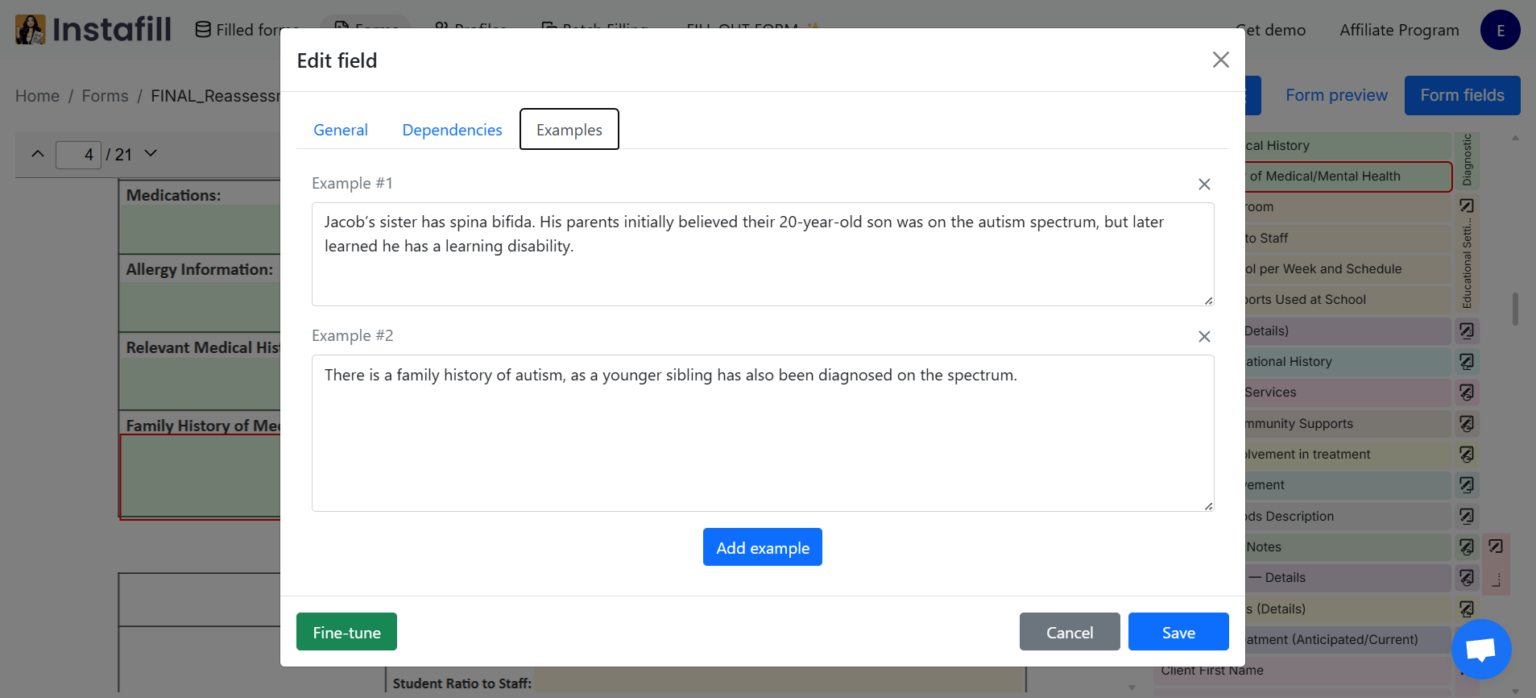
Method 2: Add examples in the Field Editor
For more control, open the Field Editor from any fine-tuned form's details page. Click "Edit" on any field, navigate to the Examples tab, and paste or type examples of how you'd write that field. 2-4 well-chosen examples per field is usually enough. There's no limit - the more you provide, the better the AI understands your style.
What happens next
When filling the form, the AI processes fields with examples individually (standard fields are filled in batches for efficiency). It analyzes your tone, vocabulary, sentence length, and formatting, then applies your voice to new content. The facts come from your source data. The voice comes from your examples.
For a detailed walkthrough with best practices, read Introducing Examples: Instafill.ai can replicate your voice
What the AI Analyzes
When you provide examples, the AI studies multiple dimensions of your writing at once:
| Dimension | What it learns |
|---|---|
| Tone and formality | Professional vs. conversational, direct vs. diplomatic |
| Vocabulary | Technical terms, industry jargon, preferred word choices |
| Sentence structure | Length, complexity, use of compound sentences |
| Formatting | Punctuation style, paragraph structure, use of lists |
You don't need to explain your style. The AI learns it from your examples. This is more effective than writing instructions like "use a conversational tone" because the AI sees exactly what "conversational" means to you.
When to Use Examples
Style Replication is valuable whenever authentic, human-written text matters in generated fields.
| Industry | Use case |
|---|---|
| ABA therapy and healthcare | Behavioral observations, progress notes, and assessment summaries generated from session transcripts that match your clinical writing voice |
| Construction | Scope of work statements, project specifications, and permit narratives that use your company's terminology and meet jurisdiction expectations |
| Legal | Incident descriptions, factual summaries, and procedural explanations that reflect your firm's writing conventions |
| Insurance | Incident descriptions and damage assessments generated from adjuster notes in your company's voice |
| HR and operations | Performance reviews and incident reports generated from notes with your organization's consistent tone |
Focus examples on narrative fields, descriptions, and explanations - fields where tone and phrasing matter. Simple fields like names, dates, and addresses don't need examples.
Examples vs. Field Descriptions
Both tools customize how fields are filled. They serve different purposes and work best together.
| Scenario | Best approach |
|---|---|
| Specify a required format (dates, phone numbers) | Field description |
| Explain conditional logic or special rules | Field description |
| Define tone, writing style, or narrative structure | Examples |
| Demonstrate specific phrasing or terminology | Examples |
| Maintain consistent voice across similar fields | Examples |
Use field descriptions for rules and constraints. Use Examples for voice and style. For best results, combine both: descriptions explain what should go in the field, and examples show how it should sound.
Common Questions
How many examples should I add per field?
2-4 well-chosen examples are usually sufficient. More examples help the AI identify consistent patterns, but beyond 4-5 you see diminishing returns.
What file formats can I upload as previously filled forms?
PDF and Word documents. Upload them alongside your blank form during setup, and the AI learns your writing style from how those forms were filled.
Should I vary my examples?
Yes. If all your examples are nearly identical, the AI may replicate too closely. Show slight variation in how you express similar ideas - this helps the AI learn your voice rather than memorize specific phrases.
Does this affect all fields on the form?
No. Only fields with examples use style replication. All other fields fill accurately using the standard AI.
Can I use this with batch processing?
Not yet. Style Replication currently works with individual form fills. Batch processing support is on our roadmap.