Yes! You can use AI to fill out Form CMS-116, CLIA Application
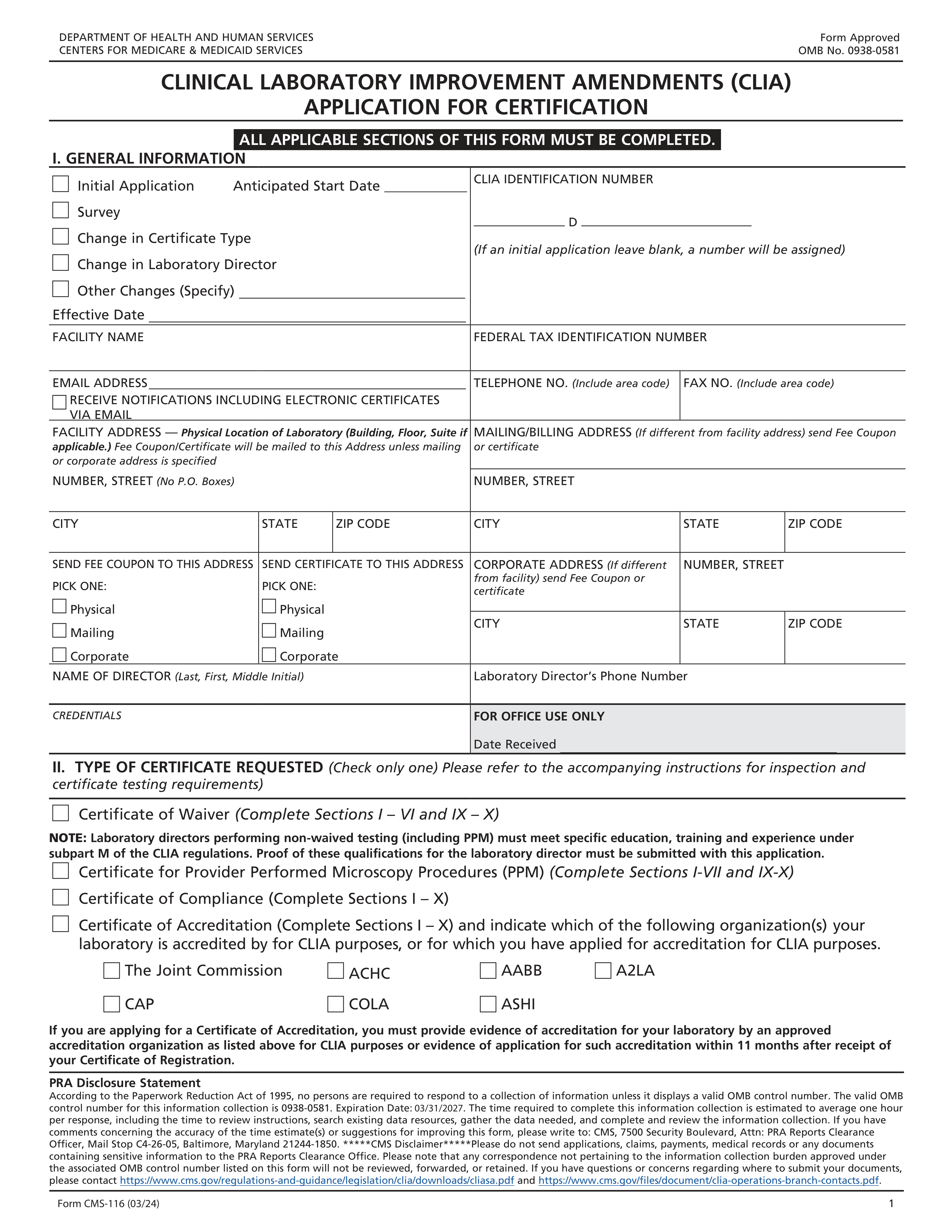
Form CMS-116 is the application for certification under the Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA). This form is crucial for laboratories that test human specimens, ensuring they meet federal standards for quality and safety in laboratory testing.
Our AI automatically handles information lookup, data retrieval, formatting, and form filling.
It takes less than a minute to fill out Form CMS-116 using our AI form filling.
Securely upload your data. Information is encrypted in transit and deleted immediately after the form is filled out.
Form specifications
| Form name: | Form CMS-116, CLIA Application |
| Form issued by: | Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services |
| Number of fields: | 297 |
| Number of pages: | 10 |
| Version: | 03/24 |
| Language: | English |
| Categories: | CMS forms |
Instafill Demo: filling out a legal form in seconds
How to Fill Out Form CMS-116 Online for Free in 2026
Are you looking to fill out a FORM CMS-116 form online quickly and accurately? Instafill.ai offers the #1 AI-powered PDF filling software of 2026, allowing you to complete your FORM CMS-116 form in just 37 seconds or less.
Follow these steps to fill out your FORM CMS-116 form online using Instafill.ai:
- 1 Visit instafill.ai site and select CMS-116.
- 2 Enter facility and contact information.
- 3 Select the type of certificate requested.
- 4 Provide details about laboratory testing and ownership.
- 5 Sign and date the form electronically.
- 6 Check for accuracy and submit the form.
Our AI-powered system ensures each field is filled out correctly, reducing errors and saving you time.
Why Choose Instafill.ai for Your Fillable Form CMS-116 Form?
Speed
Complete your Form CMS-116 in as little as 37 seconds.
Up-to-Date
Always use the latest 2026 Form CMS-116 form version.
Cost-effective
No need to hire expensive lawyers.
Accuracy
Our AI performs 10 compliance checks to ensure your form is error-free.
Security
Your personal information is protected with bank-level encryption.
Frequently Asked Questions About Form Form CMS-116
The CLIA Application form is used to apply for a Certificate of Waiver or Certificate of Compliance from the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS). This certificate allows a laboratory to perform specific tests on humans or animal specimens. The CLIA regulations ensure that laboratories meet specific requirements to provide accurate and reliable test results.
The following information is required for a CLIA certificate of waiver application: 1. Laboratory name and address, 2. Type of tests to be performed, 3. Name and qualifications of the laboratory director, 4. Description of the laboratory's quality control program, 5. Description of the laboratory's record keeping system, 6. Description of the laboratory's equipment, and 7. Signature of the laboratory director.
Laboratory directors must have a minimum of a bachelor's degree in a relevant scientific field or have completed a CLIA-approved training program. They must also have experience in the specific tests they will be performing and be able to demonstrate proficiency in those tests. Additionally, they must complete continuing education requirements to maintain their certification.
A Certificate of Compliance (CoC) is issued to laboratories that meet the minimum requirements of the CLIA regulations. A Certificate of Accreditation (CoA) is issued by an accrediting organization, such as the College of American Pathologists (CAP), that has additional requirements beyond the CLIA regulations. A laboratory can have both a CoC and a CoA.
CLIA regulations apply to all laboratories that perform tests on humans or animal specimens, except for those performing only the following tests: 1. Office laboratories performing tests for the sole purpose of diagnosing and treating the laboratory's patients, 2. Laboratories performing tests only on specimens from the laboratory's own patients, and 3. Laboratories that are exempt under CLIA regulations, such as blood banks and certain public health laboratories.
The Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA) regulations define waived tests as those that pose no more than a minimal risk to patient health and safety if the tests are performed in accordance with the instructions in the manufacturer's labeling. Waived tests do not require a CLIA certificate for the individual performing the test. Examples of waived tests include certain blood glucose tests, urinalysis, and some types of rapid tests for infectious diseases. It is important to note that even if a test is waived, the individual performing the test must still follow all other applicable state and federal regulations.
To apply for a CLIA certificate for Provider Performed Microscopy Procedures (PPM), the following steps should be taken: 1. Ensure that the individual performing the procedures meets the qualifications outlined in the CLIA regulations. 2. Complete and submit the CLIA application form, along with any required supporting documentation, to the state or accrediting agency that oversees CLIA certification in your area. 3. Pay the application fee. 4. Once the application is approved, the laboratory or healthcare facility must comply with all CLIA regulations, including maintaining quality control and quality assurance programs, and conducting proficiency testing. It is recommended that applicants review the CLIA regulations and guidance documents carefully to ensure that all requirements are met.
The estimated annual test volume requirement for a CLIA certificate application depends on the type of testing being performed and the size of the laboratory or healthcare facility. The CLIA regulations establish different volume thresholds for different types of tests and laboratories. For example, a laboratory performing high complexity tests must have a minimum annual volume of 250 tests in each of the preceding three years, while a laboratory performing moderate complexity tests may have a lower volume requirement. It is important to note that these are minimum requirements, and some states or accrediting agencies may have higher volume requirements. Applicants should review the CLIA regulations and guidance documents carefully to determine the specific volume requirement for their laboratory or healthcare facility.
Under CLIA regulations, laboratories can be classified as voluntary nonprofit, for profit, or government laboratories. The primary difference between these types of laboratories is their ownership and operational structure. Voluntary nonprofit laboratories are typically operated by nonprofit organizations, such as hospitals or public health departments, and may be exempt from certain fees and requirements. For profit laboratories are operated for the purpose of making a profit, and may be subject to additional fees and requirements. Government laboratories are operated by federal, state, or local government agencies, and may be subject to different regulations and requirements than private laboratories. It is important for applicants to understand the specific requirements that apply to their laboratory type.
Any changes to a CLIA certificate, such as a change of address, ownership, or test menu, must be reported to the state or accrediting agency that issued the certificate in a timely manner. Failure to report changes in a timely manner may result in enforcement action. To report changes, laboratories should complete and submit the appropriate form and any required supporting documentation to the state or accrediting agency. It is recommended that laboratories review the CLIA regulations and guidance documents carefully to ensure that they are aware of their reporting obligations and deadlines.
Violating the Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA) regulations can result in serious consequences for laboratories and individuals. These consequences may include: 1. Civil penalties, 2. Criminal penalties, 3. Suspension or revocation of CLIA certification, 4. Exclusion from participation in federal health care programs, such as Medicare and Medicaid. It is essential to adhere to CLIA regulations to ensure the accuracy, reliability, and timeliness of laboratory results.
State Agencies play a crucial role in the CLIA certification process. They are responsible for conducting on-site inspections of laboratories to ensure compliance with CLIA regulations. State Agencies also issue and renew CLIA certificates, as well as handle appeals and disciplinary actions. Laboratories must maintain their CLIA certification to continue operating and billing for services under federal health care programs.
A Certificate of Waiver allows certain laboratories to perform waived tests without the need for CLIA certification. These tests are considered to have a low risk of error and can be performed by qualified individuals in a variety of settings, such as physician offices and clinics. A Certificate for Provider Performed Microscopy Procedures (PPM), on the other hand, allows individual healthcare professionals to perform certain microscopy procedures on their own patients in their offices or clinics. These procedures include urinalysis, cytology, and hematology tests. It is important to note that even with a Certificate of Waiver or PPM, laboratories and healthcare professionals must still follow all applicable state and federal regulations.
The process for renewing a CLIA certificate typically involves the following steps: 1. Submitting a renewal application to the State Agency, 2. Paying the required renewal fee, 3. Providing evidence of continued compliance with CLIA regulations, such as quality control records and personnel qualifications, 4. Undergoing a re-inspection by the State Agency. It is important to renew your CLIA certificate before it expires to avoid any disruption in laboratory operations and continued participation in federal health care programs.
If a laboratory disagrees with a CLIA certification decision, it may appeal the decision through the following process: 1. Request a re-inspection or re-evaluation of the laboratory, 2. Submit a written appeal to the State Agency, 3. Request a hearing before an administrative law judge, 4. File a lawsuit in federal court. It is important to note that the appeal process can be lengthy and costly, and it is recommended that laboratories seek legal advice before initiating an appeal.
The Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA) allow a single certificate to be issued to cover multiple sites if they are under common ownership and management. Each site must be inspected and approved by the certifying agency. The laboratory must submit a single application with information about all sites, including their locations and the individuals in charge of each site. All sites must comply with CLIA regulations and meet the same requirements for accreditation and certification.
To transfer a CLIA certificate to a new owner or director, the laboratory must submit a request to the certifying agency. The new owner or director must meet the eligibility requirements for certification, including education, experience, and training. The laboratory must also provide documentation of the transfer, such as proof of ownership and a statement from the new owner or director acknowledging responsibility for the laboratory. The certifying agency will inspect the laboratory to ensure that it continues to meet CLIA regulations and will issue a new certificate with the new owner or director's information.
CLIA certified laboratories are required to maintain accurate and complete records of all tests performed, including patient information, test results, and quality control data. Records must be kept for a minimum of five years and must be made available to the certifying agency upon request. Laboratories must also maintain records of personnel training, equipment calibration and maintenance, and corrective actions taken in response to errors or discrepancies.
The fees for obtaining a CLIA certificate vary depending on the size and complexity of the laboratory and the services it offers. The fees include an application fee, an inspection fee, and an annual registration fee. The application fee covers the cost of processing the application and may include fees for each site covered under the certificate. The inspection fee covers the cost of the on-site inspection and may be based on the number of tests performed or the number of personnel at the laboratory. The annual registration fee covers the cost of maintaining the certificate and may be based on the number of tests performed or the size of the laboratory.
Compliance Form CMS-116
Validation Checks by Instafill.ai
1
Application Type Indication
Ensures that the application type is clearly indicated on the Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments Application. It checks whether the applicant has selected one of the following options: Initial Application, Survey, Change in Certificate Type, Change in Laboratory Director, or Other Changes. Additionally, it verifies that if a change is specified, an effective date is included to confirm when the change should take place.
2
CLIA Identification Number
Confirms that the CLIA IDENTIFICATION NUMBER field is left blank for initial applications. This validation is crucial as the CLIA identification number is assigned by the agency after the application is processed. The check prevents applicants from entering incorrect or placeholder numbers that could lead to processing delays or errors.
3
Facility Name and Federal Tax ID
Verifies that the FACILITY NAME and FEDERAL TAX IDENTIFICATION NUMBER are provided on the form. This check is important to ensure that the laboratory is correctly identified and associated with the correct tax information. It helps in maintaining accurate records and facilitates any necessary financial transactions or communications.
4
Email Address and Notification Preference
Checks that a valid EMAIL ADDRESS is entered on the Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments Application and that the applicant has selected their preference for receiving notifications. This includes confirming the desire to receive electronic certificates via email. The validation ensures that the laboratory will receive timely communications and official documents in their preferred format.
5
Telephone and Fax Numbers
Ensures that the TELEPHONE NO. and FAX NO. fields include the correct area codes. This validation confirms that the contact information provided is complete and can be used for reliable communication. It is essential for facilitating any follow-up calls or the transmission of documents that may be required during the application process or after certification.
6
Facility Address Validation
Ensures that the FACILITY ADDRESS field is filled with the actual physical location where the testing is performed. Confirms that the address provided is not a P.O. Box, as this is not permissible for the physical location of the facility. Validates that the address is complete, including any necessary suite or room numbers, to ensure accurate identification of the testing site. Checks for consistency in the address format to maintain data integrity.
7
Mailing/Billing Address Validation
Verifies that the MAILING/BILLING ADDRESS, along with the CITY, STATE, and ZIP CODE, are provided when they differ from the facility address. Ensures that the mailing address is complete and accurate for correspondence and billing purposes. Validates that the state and zip code are consistent with the city provided. Checks for any discrepancies between the mailing and facility addresses when they are supposed to be the same.
8
Fee Coupon and Certificate Address Selection
Checks which address (Physical, Mailing, Corporate) is selected for the SEND FEE COUPON and SEND CERTIFICATE options. Ensures that the selected address is appropriate for the intended document delivery. Confirms that the address provided for these options is complete and accurate. Verifies that if a corporate address is selected, it is indeed the correct address for corporate correspondence.
9
Corporate Address Validation
Ensures that the CORPORATE ADDRESS is provided when applicable. Validates that the corporate address is complete, including any necessary identifiers such as suite or office numbers. Confirms that the corporate address is different from the facility address if required. Checks that the corporate address is consistent with the legal entity's registered address for compliance purposes.
10
Director Information Validation
Confirms that the NAME OF DIRECTOR is correctly entered and matches the individual authorized to act in this capacity. Verifies that the phone number provided for the director is valid and reachable. Ensures that the CREDENTIALS of the director are accurately recorded, reflecting their qualifications. Checks for consistency and completeness in the director's information to maintain the integrity of the application.
11
Type of Certificate Validation
Ensures that only one type of certificate requested is selected to prevent conflicting requests. Verifies that if a Certificate of Accreditation is applied for, evidence of accreditation is attached, as this is a mandatory requirement. Checks for any discrepancies or multiple selections that could invalidate the application. Prompts for correction if more than one certificate type is checked or if accreditation evidence is missing for the Certificate of Accreditation.
12
Facility Type Indication
Confirms that the facility type is correctly indicated in the TYPE OF LABORATORY section of the application. This is crucial as it determines the regulatory requirements the laboratory must adhere to. Validates that the selection matches the services provided by the facility. Alerts the user to any inconsistencies or omissions in the facility type designation to ensure accurate processing of the application.
13
Hours of Laboratory Testing Format
Ensures that the HOURS OF LABORATORY TESTING are listed in the correct HH:MM format for clarity and standardization. Verifies that the 24/7 box is checked if the facility operates continuously, which is essential for accurate representation of operational hours. Checks for any non-standard entries or formatting errors that could lead to misunderstandings regarding the laboratory's hours of operation. Prompts for correction if the format is incorrect or if the 24/7 operation is not properly indicated.
14
Multiple Sites Section Completion
Confirms that the MULTIPLE SITES section is completed accurately if applying for a single site CLIA certificate to cover multiple testing locations. This is important for ensuring that all sites are in compliance with CLIA regulations under a single certificate. Verifies that all required information for each site is provided and that no site is omitted. Alerts the user to complete this section if it is left blank or incomplete when multiple sites are being covered.
15
Testing Sections and Annual Test Volume
Verifies that the waived, PPM (Provider-Performed Microscopy), and non-waived testing sections are fully completed, as this information is critical for determining the laboratory's testing capabilities. Ensures that the estimated total annual test volume is provided for each category, which is necessary for workload assessment and compliance purposes. Checks for any missing or implausible test volume data that could affect the laboratory's CLIA status. Prompts for correction if any testing category or annual test volume is not accurately reported.
Common Mistakes in Completing Form CMS-116
The Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA) application process requires the submission of a unique CLIA Identification Number for initial applications. Failure to provide this number may result in processing delays or even rejection of the application. To avoid this mistake, applicants should ensure they have their CLIA number readily available before beginning the application process. If an applicant does not yet have a CLIA number, they should apply for one through the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) prior to submitting their application.
The CLIA application process includes various types of certificates, such as Certificate of Waiver, Certificate for Provider Performed Microscopy Procedures, Certificate of Compliance, and Certificate of Accreditation. Failing to clearly indicate the type of certificate application can lead to processing delays or even rejection of the application. To prevent this mistake, applicants should carefully review the instructions and select the appropriate certificate type based on their laboratory's specific circumstances.
The CLIA application form includes various boxes for different types of laboratories, such as hospital laboratories, independent laboratories, and physician offices. Failing to check the appropriate box for the type of laboratory can result in processing delays or even rejection of the application. To avoid this mistake, applicants should carefully review the instructions and select the box that best describes their laboratory's type.
The CLIA application requires the submission of hours of laboratory testing for each day of the week. Neglecting to provide this information can lead to processing delays or even rejection of the application. To prevent this mistake, applicants should carefully review the instructions and accurately record the hours of laboratory testing for each day of the week.
The CLIA application requires the submission of information about waived testing and the estimated total annual test volume. Failing to provide this information can result in processing delays or even rejection of the application. To avoid this mistake, applicants should carefully review the instructions and accurately record the information about waived testing and the estimated total annual test volume for their laboratory.
Failure to mark the checkbox for each Proficiency Testing Program (PPM) procedure and indicate the estimated total annual test volume for each can result in an incomplete application. This information is crucial for the accreditation body to assess the laboratory's competence and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements. To avoid this mistake, carefully review the list of PPM procedures and mark the appropriate checkboxes. Then, provide the estimated annual test volume for each procedure to ensure a complete and accurate application.
Neglecting to identify non-waived testing, including each analyte, test system, or device used, and indicate the complexity and estimated annual test volume can lead to an incomplete application. Non-waived tests are those that require a CLIA certificate of waiver or certification. Proper identification and reporting of these tests are essential for maintaining regulatory compliance. To avoid this mistake, carefully review the testing performed by the laboratory and ensure that all non-waived tests are identified and reported, along with the analyte, test system, or device used and the estimated annual test volume.
Failure to check the appropriate box for the ownership type of the facility can result in an incorrect application. The ownership type determines the regulatory requirements for the laboratory. To avoid this mistake, carefully review the instructions and check the appropriate box based on the laboratory's ownership structure.
Omitting the CLIA number and name of any additional laboratories where the director serves as director can result in an incomplete application. This information is required for the accreditation body to assess the director's involvement in other laboratories. To avoid this mistake, ensure that all laboratories where the director serves as director are listed with their corresponding CLIA number and name.
Neglecting to provide the print name of the director of laboratory and owner of laboratory, along with their signatures and the date signed, can result in an incomplete application. These signatures are required for the accreditation body to verify the authenticity of the application. To avoid this mistake, ensure that the print names of the director and owner are provided, along with their signatures and the date signed.
One of the most critical mistakes in completing the Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA) Application form is not sending the completed form along with the required payment to the appropriate State Agency. This oversight can lead to significant delays in the application process and may result in the denial of the application. To avoid this mistake, it is essential to carefully review the instructions provided on the form and ensure that all required documents and fees are included in the submission. It is also recommended to allow sufficient time for processing and mailing to ensure timely submission.
Another common mistake in completing the CLIA Application form is providing incomplete or inaccurate information. This can include missing signatures, incorrect contact information, or unclear responses to specific questions. Incomplete applications may be returned, causing delays in the process. To avoid this mistake, it is crucial to carefully read and follow all instructions on the form, providing all necessary information in a clear and concise manner. Double-checking all entries for accuracy is also recommended.
A third mistake in completing the CLIA Application form is failing to obtain any necessary permits or approvals before submitting the application. Depending on the nature of the laboratory and its location, various permits or approvals may be required. Failing to obtain these permits or approvals can result in the denial of the application or delays in the process. To avoid this mistake, it is essential to research and understand any necessary permits or approvals and ensure they are obtained before submitting the application.
Lastly, sending the completed CLIA Application form to the wrong State Agency is a common mistake. Each State Agency has its own specific mailing address and application process. Sending the form to the incorrect agency can result in significant delays or even the denial of the application. To avoid this mistake, it is crucial to carefully review the instructions provided on the form and ensure that the completed form is sent to the correct State Agency.
Saved over 80 hours a year
“I was never sure if my IRS forms like W-9 were filled correctly. Now, I can complete the forms accurately without any external help.”
Kevin Martin Green
Your data stays secure with advanced protection from Instafill and our subprocessors



Robust compliance program
Transparent business model
You’re not the product. You always know where your data is and what it is processed for.
ISO 27001, HIPAA, and GDPR
Our subprocesses adhere to multiple compliance standards, including but not limited to ISO 27001, HIPAA, and GDPR.
Security & privacy by design
We consider security and privacy from the initial design phase of any new service or functionality. It’s not an afterthought, it’s built-in, including support for two-factor authentication (2FA) to further protect your account.
Fill out Form CMS-116 with Instafill.ai
Worried about filling PDFs wrong? Instafill securely fills cms-116 forms, ensuring each field is accurate.