Yes! You can use AI to fill out Form SSA-1042S, Social Security Benefit Statement
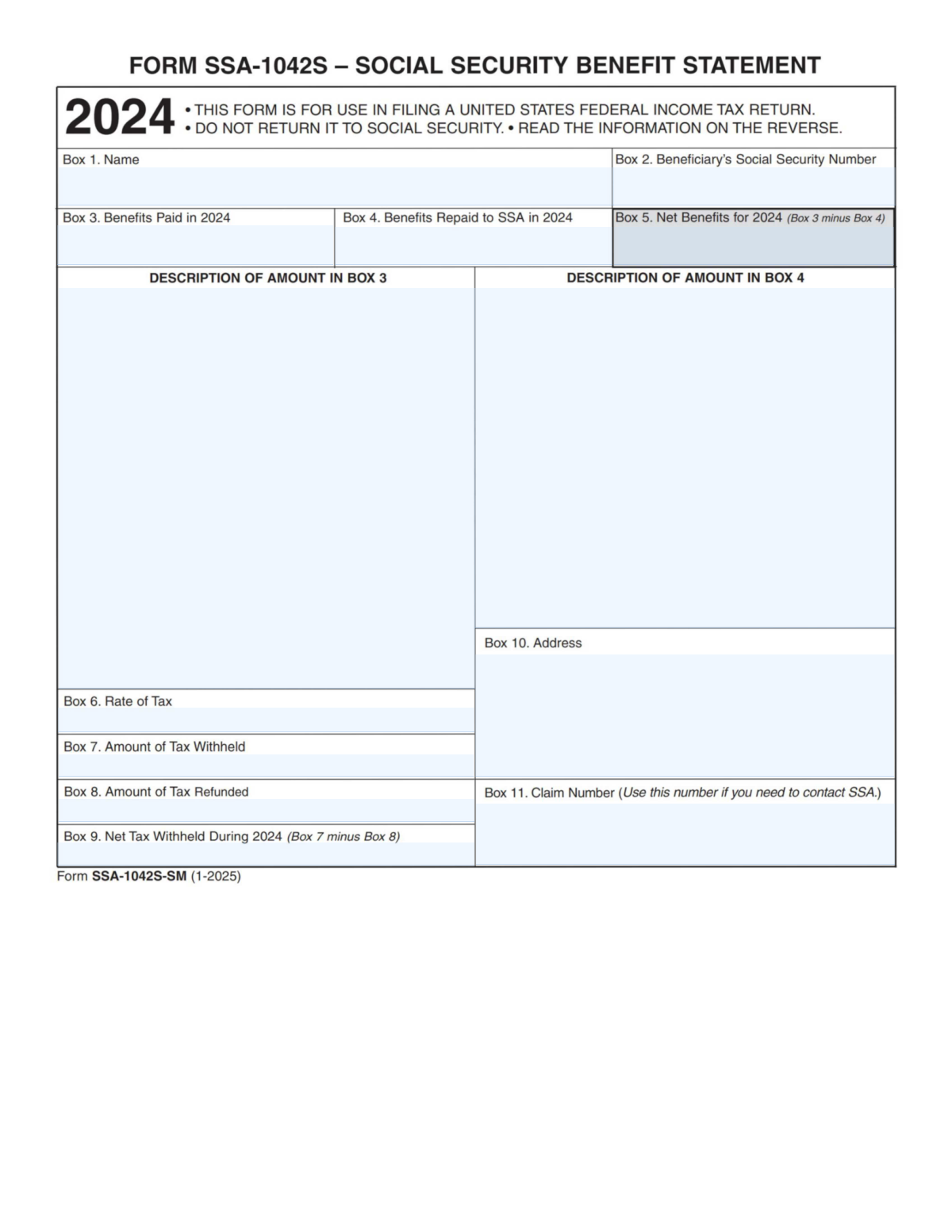
Form SSA-1042S is an annual statement issued by the Social Security Administration that summarizes Social Security benefits paid during the tax year, any benefits repaid, and any U.S. federal tax withheld or refunded. It is used to help taxpayers accurately report Social Security income and withholding on a U.S. federal income tax return. The form is informational and should not be returned to SSA; it should be kept with tax records and used for tax preparation.
Our AI automatically handles information lookup, data retrieval, formatting, and form filling.
It takes less than a minute to fill out SSA-1042S using our AI form filling.
Securely upload your data. Information is encrypted in transit and deleted immediately after the form is filled out.
Form specifications
| Form name: | Form SSA-1042S, Social Security Benefit Statement |
| Number of pages: | 1 |
| Filled form examples: | Form SSA-1042S Examples |
| Language: | English |
| Categories: | social security forms, benefit forms, SSA forms, PA state forms |
Instafill Demo: filling out a legal form in seconds
How to Fill Out SSA-1042S Online for Free in 2026
Are you looking to fill out a SSA-1042S form online quickly and accurately? Instafill.ai offers the #1 AI-powered PDF filling software of 2026, allowing you to complete your SSA-1042S form in just 37 seconds or less.
Follow these steps to fill out your SSA-1042S form online using Instafill.ai:
- 1 Enter the beneficiary’s name (Box 1) exactly as shown on official records.
- 2 Provide the beneficiary’s Social Security Number (Box 2).
- 3 Input total benefits paid for the year (Box 3) and, if applicable, benefits repaid to SSA (Box 4), then confirm net benefits (Box 5).
- 4 Review and record the descriptions associated with the amounts in Box 3 and Box 4 to ensure the correct type of payments/repayments are reflected.
- 5 Enter the tax rate (Box 6) and the amount of tax withheld (Box 7), and include any tax refunded (Box 8) to calculate net tax withheld (Box 9).
- 6 Add the beneficiary’s address (Box 10) and the SSA claim number (Box 11) for reference if contacting SSA is needed.
- 7 Download or save the completed form details and use them to populate the Social Security benefits and withholding sections of the U.S. federal income tax return.
Our AI-powered system ensures each field is filled out correctly, reducing errors and saving you time.
Why Choose Instafill.ai for Your Fillable SSA-1042S Form?
Speed
Complete your SSA-1042S in as little as 37 seconds.
Up-to-Date
Always use the latest 2026 SSA-1042S form version.
Cost-effective
No need to hire expensive lawyers.
Accuracy
Our AI performs 10 compliance checks to ensure your form is error-free.
Security
Your personal information is protected with bank-level encryption.
Frequently Asked Questions About Form SSA-1042S
Form SSA-1042S is a Social Security Benefit Statement used to help you file a U.S. federal income tax return. It reports Social Security benefits paid to you and any U.S. tax withheld or refunded during the year.
This form is generally issued to Social Security beneficiaries who had benefits paid during the year and whose benefits are reported on a 1042-S-style statement (often involving nonresident alien tax rules or withholding). If you received Social Security benefits and had tax withholding reported this way, you may get this form.
No. The form states “DO NOT RETURN IT TO SOCIAL SECURITY.” Keep it with your tax records and use it to prepare your tax return.
Most taxpayers use the amounts in Box 3 (Benefits Paid), Box 4 (Benefits Repaid), Box 5 (Net Benefits), and any withholding information in Boxes 6–9. Your name, SSN, and claim number can also help match the form to your records.
Box 3 shows the total Social Security benefits paid to you during 2024. The “Description of amount in Box 3” may explain what types of payments are included.
Box 4 shows amounts you repaid to Social Security in 2024, such as repayments of overpayments. The description line for Box 4 may provide additional detail about the repayment.
Box 5 is your net benefits for the year and is calculated as Box 3 minus Box 4. This is often the key figure used when determining taxable benefits.
Box 6 shows the tax withholding rate applied to your benefits, if withholding occurred. If no tax was withheld, this box may be blank or show a zero rate.
Box 7 is the total amount of U.S. federal tax withheld from your Social Security benefits during 2024. You may be able to claim this amount as withholding on your tax return, depending on your filing situation.
Box 8 shows any tax that was previously withheld but then refunded during 2024. This can happen if withholding was adjusted or corrected.
Box 9 is the net tax withheld for the year, calculated as Box 7 minus Box 8. This is the amount that generally reflects your final withholding after any refunds.
Box 10 shows the address Social Security has on file for you. If it’s incorrect, you should update your address with SSA to ensure you receive future statements and notices.
Box 11 is your Social Security claim number. Use it when contacting SSA about questions or corrections related to your benefits or this statement.
Contact Social Security as soon as possible to request a correction, using the claim number in Box 11 if available. Incorrect identifying information can cause problems when matching your tax records.
The form says “READ THE INFORMATION ON THE REVERSE,” meaning instructions and explanations are printed on the back. Review the reverse side for guidance on how the amounts may be used for tax filing.
Compliance SSA-1042S
Validation Checks by Instafill.ai
1
Tax Year Must Be Present and Match 2024
Validates that the statement year is present and explicitly indicates 2024 (e.g., “Benefits Paid in 2024”). This is important because all monetary boxes and withholding calculations are year-specific and must align to the taxpayer’s filing year. If the year is missing or not 2024, the submission should be rejected or flagged for manual review to prevent reporting amounts for the wrong tax year.
2
Beneficiary Name (Box 1) Completeness and Character Validation
Checks that Box 1 contains a non-empty beneficiary name with reasonable characters (letters, spaces, hyphens, apostrophes) and is not only initials or placeholder text. This matters for identity matching and downstream tax reporting, especially when reconciling with SSN and claim number. If invalid, the system should require correction because identity cannot be reliably established.
3
Beneficiary SSN (Box 2) Format and Validity Rules
Validates that the SSN is exactly 9 digits (allowing optional hyphens in the display format) and rejects known invalid patterns (e.g., all zeros in any group, 000/666/9xx in the first three digits). This is critical for taxpayer identification and preventing misapplied benefits/tax withholding. If the SSN fails validation, the submission should be blocked and routed for correction or verification.
4
Address (Box 10) Required Fields and Postal Format Validation
Ensures Box 10 includes required address components appropriate to the country context (e.g., street line, city, state/province, postal code; for U.S. addresses validate 2-letter state and 5-digit or ZIP+4). Accurate address data is important for correspondence, identity verification, and audit support. If incomplete or malformed, the system should flag the record and request a corrected address.
5
Monetary Amount Fields Must Be Numeric, Non-Negative, and Currency-Formatted
Validates that Boxes 3, 4, 5, 7, 8, and 9 contain numeric values with at most two decimal places and are not negative. This prevents parsing errors and ensures consistent financial calculations and reporting. If any amount is non-numeric, has excessive decimals, or is negative, the submission should fail validation and require correction.
6
Net Benefits Calculation (Box 5 = Box 3 − Box 4)
Checks that Box 5 equals Box 3 minus Box 4 within an acceptable rounding tolerance (e.g., $0.01). This is essential because Box 5 is a derived value used for tax reporting and must reconcile to the paid and repaid amounts. If the calculation does not match, the system should flag the discrepancy and either recompute Box 5 or require the submitter to correct the inputs.
7
Benefits Repaid (Box 4) Cannot Exceed Benefits Paid (Box 3)
Validates that Box 4 is less than or equal to Box 3, since repaid benefits for the year should not exceed benefits paid for the same year on the statement. This logical constraint prevents negative net benefits and indicates potential data entry or extraction errors. If Box 4 > Box 3, the submission should be rejected or escalated for manual review.
8
Tax Rate (Box 6) Format and Range Validation
Ensures Box 6 is present when withholding is reported and is expressed as a percentage or decimal in an expected range (e.g., 0%–100% or 0.00–1.00 depending on representation). This matters because the rate supports reasonableness checks against withheld amounts and helps detect mis-keyed values (e.g., 30 entered as 0.30 or vice versa). If out of range or malformed, the system should flag the record and require normalization or correction.
9
Withholding Amount (Box 7) Consistency with Benefits Paid (Box 3)
Validates that Box 7 (tax withheld) is not greater than Box 3 (benefits paid) and is reasonable given the tax rate in Box 6 (if provided). This prevents impossible withholding scenarios and catches common OCR/data-entry errors. If Box 7 exceeds Box 3 or is inconsistent with Box 6 beyond tolerance, the submission should be flagged for review.
10
Tax Refunded (Box 8) Cannot Exceed Tax Withheld (Box 7)
Checks that Box 8 is less than or equal to Box 7, since refunded tax should not exceed the amount originally withheld. This is important for accurate net withholding and to prevent negative or inflated refund reporting. If Box 8 > Box 7, the submission should be rejected or sent to exception handling.
11
Net Tax Withheld Calculation (Box 9 = Box 7 − Box 8)
Validates that Box 9 equals Box 7 minus Box 8 within a small rounding tolerance. This ensures internal consistency and prevents downstream tax reporting errors where net withholding is used. If the values do not reconcile, the system should recompute Box 9 or require correction before acceptance.
12
Conditional Presence: Tax Fields Required When Any Withholding/Refund Is Reported
If any of Boxes 6–9 contain a value, validates that the related fields needed to interpret them are present (e.g., if Box 7 or 8 is present, Box 9 must be present or computable; if Box 7 is present, Box 6 should be present unless explicitly allowed to be blank). This prevents partial submissions that cannot be interpreted reliably. If conditional requirements are not met, the submission should be flagged and returned for completion.
13
Claim Number (Box 11) Presence and Format Validation
Ensures Box 11 is present and matches expected claim number patterns (commonly an SSN-derived identifier with a suffix, or other SSA claim formats), allowing only valid characters and lengths. This is important for contacting SSA and for internal reconciliation when SSN or name discrepancies exist. If missing or malformed, the system should flag the record because it reduces traceability and may indicate extraction errors.
14
Cross-Field Identity Consistency: SSN (Box 2) vs Claim Number (Box 11)
Where applicable, validates that the claim number is consistent with the beneficiary SSN (e.g., claim number begins with the SSN or otherwise matches expected linkage rules) and that both are not conflicting identifiers. This helps detect swapped fields, OCR mistakes, or identity mismatches. If inconsistent, the submission should be routed to manual review and not auto-posted.
15
Descriptions for Amounts (Boxes 3 and 4) Must Be Present When Amounts Are Non-Zero
Validates that the “DESCRIPTION OF AMOUNT IN BOX 3” and/or “DESCRIPTION OF AMOUNT IN BOX 4” sections are populated when the corresponding amount is non-zero, if the form design expects explanatory text. This matters for auditability and for interpreting special payment/recovery situations. If an amount is non-zero but the description is missing, the system should flag the submission for completion or review.
Common Mistakes in Completing SSA-1042S
People often treat this like a form that must be returned because it looks official and includes multiple boxes. Sending it to SSA can delay your tax filing and does not satisfy any IRS requirement. Keep the statement for your records and use it to prepare your U.S. federal income tax return; do not mail it to SSA.
Taxpayers sometimes pull numbers from a different year’s statement or from monthly benefit notices, especially if they have multiple SSA letters. This leads to incorrect income reporting and potential IRS notices or amended returns. Confirm the statement is for 2024 and use the amounts specifically labeled “in 2024” for Boxes 3, 4, 5, and 9.
A common error is transposing digits, using a spouse’s SSN, or entering an ITIN instead of the beneficiary’s SSN. A mismatch can cause e-file rejections, processing delays, or IRS identity/verification issues. Copy the SSN exactly as shown in Box 2 and ensure it matches the taxpayer record on the return.
Because Box 3 is prominent, filers often report the gross benefits paid even when there were repayments in Box 4. This can overstate taxable benefits and increase tax unnecessarily. If Box 4 is not zero, use Box 5 (Box 3 minus Box 4) as the net benefits figure when your tax software or preparer asks for net benefits.
Repayments are easy to miss because they may relate to prior overpayments or adjustments and are described separately. Ignoring Box 4 can cause you to overreport income and lose the benefit of the repayment adjustment. Review the “Description of amount in Box 4” and ensure the repayment is reflected by using Box 5 or by following your tax software’s specific prompts for repayments.
People often enter Box 7 as the final withholding without subtracting any refund shown in Box 8, or they accidentally add the two. This results in incorrect credit for withholding and can change the refund/balance due. Use Box 9 (Box 7 minus Box 8) as the net tax withheld during 2024 when your return asks for withholding from this statement.
Box 6 is a rate, but filers sometimes type it into a field expecting dollars, or they enter “30” instead of “0.30” (or vice versa) depending on the software. This can distort withholding calculations or cause validation errors. Only enter Box 6 if your tax software specifically requests the rate, and follow the software’s format guidance (percent vs. decimal).
Taxpayers sometimes assume the address on the statement is automatically correct for IRS purposes or use it to populate their return even if they moved. This can lead to missed IRS correspondence or mismatched records in tax software. Verify Box 10 against your current mailing address and update your tax return and SSA records separately if needed.
Because both are identifiers, people sometimes enter the claim number where an SSN is required or provide it to a preparer as the primary ID. This can cause e-file rejections or misapplied records. Use Box 2 for the SSN on the tax return, and use Box 11 only when contacting SSA about the statement.
Filers often skip the descriptions, assuming the totals are self-explanatory, but the descriptions may clarify what is included (e.g., specific benefit types or adjustments). Missing these details can lead to misclassification or confusion when reconciling amounts with other records. Read the descriptions to confirm what the totals represent and keep them with your tax documentation in case of questions.
Saved over 80 hours a year
“I was never sure if my IRS forms like W-9 were filled correctly. Now, I can complete the forms accurately without any external help.”
Kevin Martin Green
Your data stays secure with advanced protection from Instafill and our subprocessors



Robust compliance program
Transparent business model
You’re not the product. You always know where your data is and what it is processed for.
ISO 27001, HIPAA, and GDPR
Our subprocesses adhere to multiple compliance standards, including but not limited to ISO 27001, HIPAA, and GDPR.
Security & privacy by design
We consider security and privacy from the initial design phase of any new service or functionality. It’s not an afterthought, it’s built-in, including support for two-factor authentication (2FA) to further protect your account.
Fill out SSA-1042S with Instafill.ai
Worried about filling PDFs wrong? Instafill securely fills form-ssa-1042s-social-security-benefit-statement forms, ensuring each field is accurate.